Yantra Prakarana
Meaning of term Yantra (यन्त्र).—n.
A machine in general, any
implement or apparatus
Ref: Cologne Digital Sanskrit Dictionaries:
Shabda-Sagara Sanskrit-English Dictionary
"Yantra" in rasashastra are the those instruments/apparatus designed by the acharyas as
a result of contrivance obtained
from their experinces. These instruments help the practioners to do various
processing of rasaushadhi in a controlled mechano-thermal activities. The
ingredients and raw materials used for crafting of these yantras are so
specific that to obtain ultimate optimum yield and quality. Apparatus with same
principle are being used even now a days,with some basic modifications.
1.
Dolayantra
2.
Damaru Yantra
3.
Swedani YAntra
4.
Sthali Yantra
5.
Palika Yantra
6.
Urdhwa patina Yantra
7.
Adha patina Yantra
8.
Tiryak Patana Yantra
9.
Valuka Yantra
10.
Kachapa Yantra
11.
Vidyadhara YAntra
12.
Ullukhala Yantra
13.
Tula Yantra
14.
Patala Yantra
Dolayantra
Meaning of Term Dola
According to sanskrit dictionary
Dola
(दोल).—[dul-ghañ]
1) Swinging,
rocking, oscillating; वेलादोलानिलचलम् (velādolānilacalam) Mb.1.21.1.
2) A
swing, litter.
DDSA:
The practical Sanskrit-English dictionary
According to Budhism
dolā : (f.) a
swing; palanquin
BuddhaSasana: Concise Pali-English
Dictionary
BuddhaSasana: Concise Pali-English Dictionary
According to Shilpa shastra
Dolā
(दोला) or Dolāhasta refers
to “dangling”
Shodhganga:
The significance of the mūla-beras (śilpa)
Introduction
Dolayantra , is one of such apparatus which are in frequent
use even now a days .
In the present era; even though there are slight
modifications have happened in the material used, but the basic concept or the
basic structure of this apparatus remained same.
When we go through the above
references (Meaning) it can be understood that the as ,here in this apparatus ,
the drug is suspended on a wooden rod inside the mud pot resembling the shape
of Swing/Pendulum/palanquin ,it is name as Dola Yantra
Reference
द्रवद्रव्येण
भाण्डस्य पूरितार्धोदरस्य च।
मुखस्योभयतो
द्वारद्वयं कृत्त्वा प्रयत्नतः ॥
तयोस्तु
निक्षिपेद्दण्डं तन्मध्ये रसपोट्टलीम्।.
बध्वा तु स्वेदयेदेतद्दोलायन्त्रमिति
स्मृतम्
(Ra
ra sa /9/3-4)
Diagram
![]()
![]()
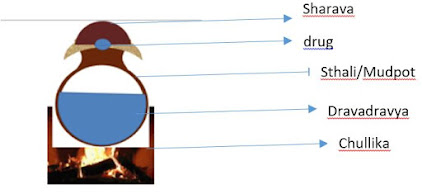
Construction
A clean mud pot of sufficient
size is taken and filled half with dravadravya (Drava dravya is the liquid used
as media while processing the drug , it can be any of the liquid media Kashaya,
Swarasa,gomutra,godugdha etc, Type of dravadravya defers as per the nature of
drug to be processed)
Two holes are made at the neck
portion of the mud pot which are at opposite to each other
Through that holes one small
wooden rod is placed and a pottali is tied at the middle of the rod in sucha a
way that pottali must be susupended at the centre of the mud pot
The whole apparatus is placed
over a furnace / Stove and heated in mandagni
While dong paka
The pottali should neither touch
the botoom of the vessel nor it must be susupended above the dravadravya
coloumn
Mandagni should be maintained
through out the process
When the process isdone for
longer duration, the dravadravya must be replenished as per need
Use
To do swedana of various drugs
Shodhana of VAtsanabhi
Shodhana Of Shanka
Swedani Yantra
As the name suggest ,
this Yantra or apparatus is used for doing Swedana of drugs , the term meaning
of “Swedani” in Monier and Williams dictionary is given as , boiler /cooking Here
in this apparatus drug is subjected to vapours of the dravadravya for specific
time.
Reference
साम्बुस्थालीमुखाबद्धे
वस्त्रे पाक्यं निवेशयेत् ।
पिधाय
पच्यते तत्र स्वेदनी यन्त्रमुच्यते
Ra
ra sa 9/5
Diagram
Construction
·
A pot is taken and it is filled with liquid.
·
It is covered with a cloth which is fastened
with a strong thread at the neck of the pot.
·
The material to be subjected for purification is
spread on the cloth and closed with a sarāva (earthen plate ) joints are sealed
with mud-smeared cloth pieces.
·
After the sealing is dried, the set is kept on
the stoveaand heated up to the time
mentioned
·
Later after cooling , the pot is taken from
stove and the processed drug is collected carefully
While doing paka
·
Mandagni must be maintained
·
If the dravadravya as drugs like ksheera,
gomutra etc then its is better to fill half to avoid the spillage
Use
Guggulu shodhanam
Damaru
Yantra
Introduction
Damdaru is an muscical instrument used for percussion. It is believd that Lord Shiva have been using this instrument during his Tandava Dance. As the shape of the apparatus resembles that of this Damaru vadya, this Yantra is named as Damaru Yantra. This Yantra has been used for Various karmas in Rasashastra
Reference
यन्त्रस्थाल्युपरि स्थालीं
न्युब्जां दत्वा निरुन्धयेत् ।
यन्त्रम् डमरुकाख्यं
तद्रसभस्मकृते हितं ॥
Explanation
Two mud pots of
similar shape and size are selected
In one mud pot the raw material to be processed are placed
and second mud pot is place over the first one upside down, in such a way that
mouth/orifice of both mud pots joints together
The joints are sealed with mud smeared cloth (sandhi bandhana
with Mrit vastra) and the dried in shade
Whole apparatus is taken and place over a furnace carefully
(mud pot which contains the drug (lower mud pot ) must come in contact with
agni)
Paka is done for the prescribed time period , and after that
it is allowed to cool and drug is collected form the inner part of upper pot.
Diagram
Uses
Parada bhasmeekarana
Rasapushpa Nirmaana
Pātana Yantra
According to the text Budha Sassana, Concise
Pali-English Dictionary, meaning of term Pātana is
mentioned as Falling/ bringing down /killing. According to the text book “The
Alchemical Body by David Gordon white, Pātana, the “sublimation” or “distillation” of
mercury refers to the three processes by which mercury is distilled upwards,
downwards, or transversally.
This
apparatus is very much used in processing of Parada, especially in the Paatana
Samskara (one of the samskara in Ashtasamskara). This apparatus is mainly used
to separate parade from other ingredients. When the mixture of drug is processed
in this apparatus parada will sublimated and separates out.
There are
three types of Pātana Yantra
a )Urdhwa
patana Yantra
b) Adha
patana Yantra
c) Tiryak
Patana Yantra
these
instruments are names as per the direction in which the separation (patana)
takes place. In urdhwa patana yantra
during the process parade will get separated to upward direction and
will get settled in the upper part of the apparatus while in the other two it
is in towards the downward direction and sidewards subsequently.
Urdhwa patana yantra
Reference
अष्टाङ्गुल
परिणाहमानाहेन दशाङ्गुलं ।
चतुरङ्गुलोत्सेधं
तोयाधारम् गलदधः ॥
अधोभाण्ड
मुखं तस्य भाण्डस्योपरिवर्त्तिनः ।
षोडशाङ्गुलविस्तीर्णपृष्टस्यास्ये
प्रवेशयेत् ॥
पार्श्वयोर्महिषिक्षीरचूर्णमण्डूर
फाणितैः ।
लिप्त्वा
विशोषयेत् सन्धिं जलाधारे जलं क्षिपेत् ।
चुल्ल्यामारोपयेदेतत्पातनायन्त्रमुच्च्यते
Ra ra sa
Two mud pots of same size
and shape are taken
In one mud pot (lower pot )
raw drug to be processed is placed and
second mud pot (upper pot ) is placed over the lower pot upside down and joints
are sealed properly wih mrit vastra(mud smeared cloth)
On the external part of
upper pot a construction of 8 angula width and 10 angula length and 4 angula height is constructed carefully.
Joints of pot and the
qualdrilateral tank (Toyadhaara) constructed must be sealed with , mahishi
dugdha bhavita combination of Quicklime
,Mandura and Phanita.
Care fully this whole
apparatus is place over chullika/Stove, water is filled in the Toyadhara and
then paka is done theekshnagni for specific time.
Diagram
Uses
Urdhwapatana of Parada
Adhapatana Yantra
Introduction
Adhapatana Yantra is one
among three types of Patana yantra.
In this yantra the raw
material to be processed is placed in the upper pot and the separation takes
place in downward direction.
Reference
अथोर्ध्वभाजने लिप्तस्थापितस्य जले सुधीः ।
दीपतैर्वनोपलः कुर्यादधः पातं प्रयत्नतः ॥
ra ra sa
Two
mud pots of same size and shape are taken
In
one mud pot (lower pot ) water is filled
up to half of its capacity and second
mud pot (upper pot ) is placed over the lower pot upside down in which the
inner portion is applied with the paste of raw material to be processed and
joints are sealed properly wih mrit vastra(mud smeared cloth).
The
whole apparatus is place in a pit dug is as per the diameter and height of
appararus ,pit must be dug in such a height that the small portion of upper pot
must be exposed out on which the Upalas are ket of ignited.
Process
is continued for specific time and after which the apparatus is carefully taken
(after cooling ) and product is obtained from the bottom portion of lower pot.
Diagram
Tiryak Patana Yantra
Introduction
Tiryakpatana Yantra is one
among three types of Patana yantra.
In this yantra the raw
material to be processed is placed in the upper pot and the separation takes
place in sideward direction.
Distillation apparatus is
often compared to this yantra, or rather Tiyakpatana yantra can be considered
as the primitive stage of Distillaion apparatus
Reference
क्षिपेद्रसं
घटे दीर्घे नताधोनालसंयुते ।
तन्नालं
निक्षिपेद्न्यघट कुक्ष्यान्तरे खलु ॥
तत्र
रुध्वा मृदा सम्यग्वदने घटयोरधः ।
अधस्ताद्रस
कुम्भस्य ज्वालयेत्तीव्रपावकम् ॥
इतरस्मिन्
घटे तोयं प्रक्षिपेत्स्वादु शीतलम् ।
तिर्यक्पातनमेतद्धिः
वार्त्तिकैरभिधीयते ॥
Two
mud pots are taken here ,one is bigger one with elongated shape (neck portion
is longer than normal )second pot is smaller pot
Rasa
/Parada to be processed is placed in deergha ghata (big pot) and at the neck
portionof the pot a small hole is made carefully
Through
which a appropriate sized hollow bamboo reed is inserted and the second end of
reed is place to the centre of second small pot
Both
mud pots are closed with lids and all the joints are sealed with mud smeared
cloth
Paka
is done to bigger pot (Pot which contains parada)
Smaller
pot is cooled down frequently by sprinkling sheeta jala over it.
After processing for prescribed time, small pot is taken carefully a lid is removed and parada is collected
Diagram
Uses
Parada samskara






No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.